前文:
- C#基础-1-标识符与数据类型
- C#基础-2-类型转换、变量与常量
- C#基础-3-运算符与判断
- C#基础-4-循环与封装
- C#基础-5-方法与可空类型
- C#基础-6-数组和Array类
- C#基础-7-字符串与String类
- C#基础-8-结构体与枚举
- C#基础-9-类与函数
继承是面向对象程序设计中最重要的概念之一。继承允许 根据一个类来定义另一个类,这使得创建和维护应用程序变得更容易。同时也有利于重用代码和节省开发时间。
当创建一个类时,程序员不需要完全重新编写新的数据成员和成员函数,只需要设计一个新的类,继承了已有的类的成员即可。这个已有的类被称为 基类,这个新的类被称为 派生类。
继承的思想实现了 属于(IS-A) 关系。例如,哺乳动物 属于 动物,狗 属于 哺乳动物,因此狗 属于 动物。
基类和派生类
一个类可以继承自另一个类,被称为基类(父类)和派生类(子类)。
C# 不支持类的多重继承,但支持接口的多重继承,一个类可以实现多个接口,即一个类可以继承多个接口,但只能继承自一个类。语法:
<访问修饰符> class <基类>
{
...
}
class <派生类> : <基类>
{
...
}
派生类会继承基类的成员(字段、方法、属性等),除非它们被明确地标记为私有 private 。派生类可以通过关键字 base 来调用基类的构造函数和方法:
class BaseClass
{
public void SomeMethod()
{
// 函数体
}
}
class DerivedClass : BaseClass
{
public void AnotherMethod()
{
// 访问基类的函数
base.SomeMethod();
// 函数体
}
}
实例:
using System;
namespace InheritanceApplication
{
class Shape
{
public void SetWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
public void SetHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected int width;
// protected 是只允许子类访问基类的变量或方法,其他类无法访问
protected int height;
}
// 派生类
class Rectangle: Shape
{
public int GetArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
}
class RectangleTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle Rect = new Rectangle();
Rect.SetWidth(5);
Rect.SetHeight(7);
// 打印对象的面积
Console.WriteLine($"总面积: {Rect.GetArea()}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
总面积: 35
相当于不用重复实例化类,可以通过实例化一次子类,就可以调用子类和父类中的所有可以调用的方法。
protected是只允许子类访问基类的变量或方法,其他类无法访问,比private更开放(允许子类访问),比public更安全(限制外部访问)。
基类的初始化
派生类继承了基类的成员变量和成员方法,因此父类对象应在子类对象创建之前被创建,可以在成员初始化列表中进行父类的初始化:
using System;
namespace RectangleApplication
{
class Rectangle
{
// 成员变量
protected double length;
protected double width;
public Rectangle(double l, double w)
{
length = l;
width = w;
}
public double GetArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void Display()
{
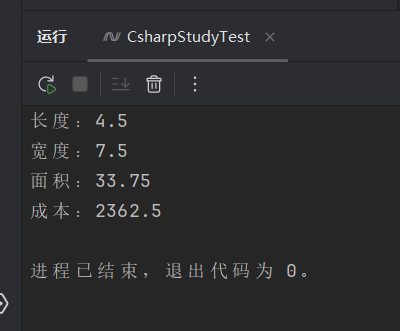
Console.WriteLine($"长度:{length}");
Console.WriteLine($"宽度:{width}");
Console.WriteLine($"面积:{GetArea()}");
}
}
class Tabletop : Rectangle
{
// private double cost;
public Tabletop(double l, double w) : base(l, w)
{ }
public double GetCost()
{
double cost;
cost = GetArea() * 70;
return cost;
}
public new void Display()
{
base.Display();
Console.WriteLine($"成本:{GetCost()}");
}
}
class ExecuteRectangle
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 在实例化子类时,把参数传给构造函数的变量 l 和 w
Tabletop t = new Tabletop(4.5, 7.5);
t.Display();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
输出:
继承接口
接口可以参见: C#基础-11-运算符重载与接口
继承接口(Interface Inheritance):一个接口可以继承自一个或多个其他接口,派生接口继承了 基接口 的所有成员,派生接口可以扩展基接口的成员列表,但不能改变它们的访问修饰符。语法:
interface IBaseInterface
{
void Method1();
}
interface IDerivedInterface : IBaseInterface
{
void Method2();
}
继承接口的实例可以通过以下方式来实现:
using System;
// 定义一个基接口
interface IBaseInterface
{
void Method1();
}
// 定义一个派生接口,继承自基接口
interface IDerivedInterface : IBaseInterface
{
void Method2();
}
// 实现派生接口的类 MyClass
class MyClass : IDerivedInterface
{
public void Method1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1 implementation");
}
public void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2 implementation");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建 MyClass 类的实例
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
// 调用继承自基接口的方法
obj.Method1();
// 调用派生接口新增的方法
obj.Method2();
}
}
以上 MyClass 类实现了 IDerivedInterface 接口,因此必须提供 IDerivedInterface 中定义的所有方法,包括从 IBaseInterface 继承的 Method1() 方法,在 Main 方法中,创建了 MyClass 的实例 obj 并调用了它的方法,输出结果为:
Method1 implementation
Method2 implementation
多重继承
多重继承指的是一个类别可以同时从多于一个父类继承行为与特征的功能。
与单一继承相对,单一继承指一个类别只可以继承自一个父类,虽然 C# 不支持多重继承,但是可以使用接口来实现多重继承:
using System;
namespace InheritanceApplication
{
class Shape
{
public void SetWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
public void SetHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
protected int width;
protected int height;
}
// 基类 PaintCost
public interface PaintCost
{
int GetCost(int area);
}
// 派生类
class Rectangle : Shape, PaintCost
{
public int GetArea()
{
return (width * height);
}
public int GetCost(int area)
{
return area * 70;
}
}
class RectangleTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle Rect = new Rectangle();
int area;
Rect.SetWidth(5);
Rect.SetHeight(7);
area = Rect.GetArea();
// 打印对象的面积
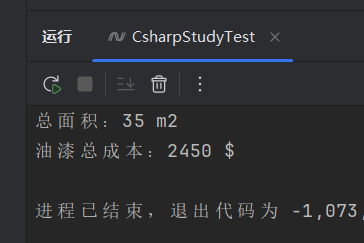
Console.WriteLine($"总面积:{Rect.GetArea()} m2");
Console.WriteLine($"油漆总成本:{Rect.GetCost(area)} $");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
多态性
多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力。
多态性意味着有多重形式。在面向对象编程范式中,多态性往往表现为"一个接口,多个功能"。
多态性可以是静态的或动态的。在静态多态性中,函数的响应是在编译时发生的。在动态多态性中,函数的响应是在运行时发生的。
在 C# 中,每个类型都是多态的,因为包括用户定义类型在内的所有类型都继承自 Object。
例如:按下 F1 键这个动作:
- 如果当前在 Flash 界面下弹出的就是 AS 3 的帮助文档;
- 如果当前在 Word 下弹出的就是 Word 帮助;
- 在 Windows 下弹出的就是 Windows 帮助和支持。
同一个事件发生在不同的对象上会产生不同的结果。
静态多态性
在编译时,函数和对象的连接机制被称为早期绑定,也被称为静态绑定。C# 提供了两种技术来实现静态多态性。分别为:函数重载和运算符重载。
函数重载
可以在同一个范围内对相同的函数名有多个定义。函数的定义必须彼此不同,可以是参数列表中的参数类型不同,也可以是参数个数不同。不同重载只有返回类型不同的函数声明。
实例:
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
public class TestData
{
public int Add(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestData dataClass = new TestData();
int add1 = dataClass.Add(1, 2);
int add2 = dataClass.Add(1, 2, 3);
Console.WriteLine($"add1 : {add1}");
Console.WriteLine($"add2 : {add2}");
}
}
}
输出:
add1 : 3
add2 : 6
又或者:
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
class Printdata
{
void print(int i)
{
Console.WriteLine($"输出整型: {i}");
}
void print(double f)
{
Console.WriteLine($"输出浮点型: {f}");
}
void print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine($"输出字符串: {s}");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Printdata p = new Printdata();
// 调用 print 来打印整数
p.print(1);
// 调用 print 来打印浮点数
p.print(1.23);
// 调用 print 来打印字符串
p.print("Hello");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
输出整型: 1
输出浮点型: 1.23
输出字符串: Hello
运算符重载
可以参见:C#基础-11-运算符重载与接口
动态多态性
C# 允许使用关键字 abstract 创建 抽象类,用于提供接口的部分类的实现。
当一个派生类继承自该抽象类时,实现即完成。
抽象类包含 抽象方法,抽象方法可被派生类实现,派生类具有更专业的功能。
有关抽象类的一些规则:
- 不能创建一个抽象类的实例。
- 不能在一个抽象类外部声明一个抽象方法。
- 通过在类定义前面放置关键字
sealed,可以将类声明为 密封类。当一个类被声明为sealed时,它不能被继承。抽象类不能被声明为sealed。
抽象类实例:
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
abstract class Shape
{
abstract public int area();
}
class Rectangle: Shape
{
private int length;
private int width;
public Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0)
{
length = a;
width = b;
}
public override int area ()
{
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle 类的面积:");
return (width * length);
}
}
class RectangleTester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 7);
double a = r.area();
Console.WriteLine($"{a}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
Rectangle 类的面积:
70
当有一个定义在类中的函数需要在继承类中实现时,可以使用 虚方法。虚方法是使用关键字 virtual 声明的。
- 虚方法可以在不同的继承类中有不同的实现。
- 对虚方法的调用是在运行时发生的。
- 动态多态性是通过 抽象类 和 虚方法 实现的。
以下实例创建了 Shape 基类,并创建派生类 Circle 、 Rectangle 、Triangle , Shape 类提供一个名为 Draw 的虚拟方法,在每个派生类中重写该方法以绘制该类的指定形状:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Shape
{
public int X { get; private set; }
public int Y { get; private set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public int Width { get; set; }
// 虚方法
public virtual void Draw()
{
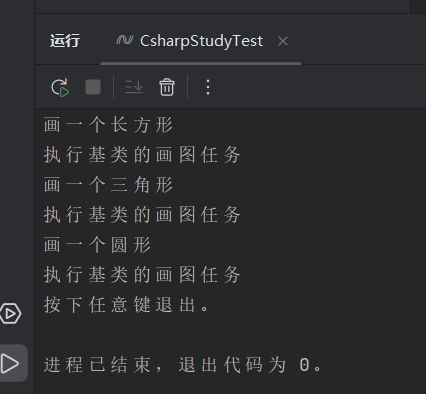
Console.WriteLine("执行基类的画图任务");
}
}
class Circle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个圆形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Rectangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个长方形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Triangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("画一个三角形");
base.Draw();
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建一个 List<Shape> 对象,并向该对象添加 Circle、Triangle 和 Rectangle
var shapes = new List<Shape>
{
new Rectangle(),
new Triangle(),
new Circle()
};
// 使用 foreach 循环对该列表的派生类进行循环访问,并对其中的每个 Shape 对象调用 Draw 方法
foreach (var shape in shapes)
{
shape.Draw();
}
Console.WriteLine("按下任意键退出。");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
输出:
通过虚方法 area() 来计算不同形状图像的面积:
using System;
namespace PolymorphismApplication
{
class Shape
{
protected int width, height;
public Shape( int a=0, int b=0)
{
width = a;
height = b;
}
public virtual int area()
{
Console.WriteLine("父类的面积:");
return 0;
}
}
class Rectangle: Shape
{
public Rectangle( int a=0, int b=0): base(a, b)
{
}
public override int area ()
{
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle 类的面积:");
return (width * height);
}
}
class Triangle: Shape
{
public Triangle(int a = 0, int b = 0): base(a, b)
{
}
public override int area()
{
Console.WriteLine("Triangle 类的面积:");
return (width * height / 2);
}
}
class Caller
{
public void CallArea(Shape sh)
{
int a;
a = sh.area();
Console.WriteLine($"面积:{a}");
}
}
class Tester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Caller c = new Caller();
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10, 7);
Triangle t = new Triangle(10, 5);
c.CallArea(r);
c.CallArea(t);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
Rectangle 类的面积:
面积:70
Triangle 类的面积:
面积:25