前文:
- C#基础-1-标识符与数据类型
- C#基础-2-类型转换、变量与常量
- C#基础-3-运算符与判断
- C#基础-4-循环与封装
- C#基础-5-方法与可空类型
- C#基础-6-数组和Array类
- C#基础-7-字符串与String类
- C#基础-8-结构体与枚举
- C#基础-9-类与函数
- C#基础-10-继承与多态性
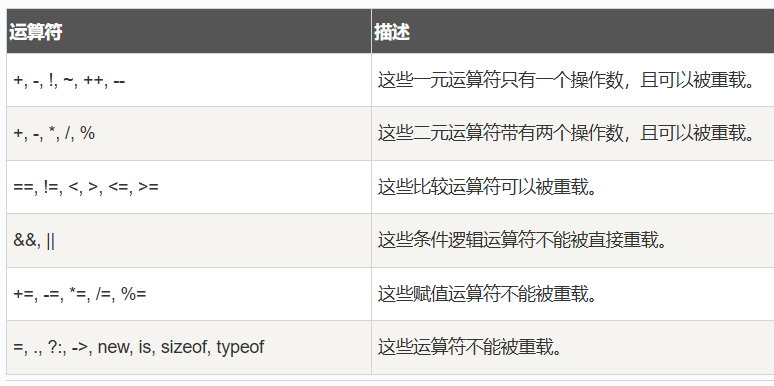
运算符重载
可以允许重定义或重载 C# 中内置的运算符。
因此,程序员也可以使用用户自定义类型的运算符。
重载运算符是具有特殊名称的函数,是通过关键字 operator 后跟运算符的符号来定义的。
与其他函数一样,重载运算符有返回类型和参数列表。
例如:
public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.length = b.length + c.length;
box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth;
box.height = b.height + c.height;
return box;
}
该示例给自定义的类 Box 实现了加法运算符 + 。它把两个 Box 对象的属性相加,并返回相加后的 Box 对象。
实例:
using System;
namespace OperatorOvlApplication
{
class Box
{
private double length; // 长度
private double breadth; // 宽度
private double height; // 高度
public double GetVolume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
public void SetLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public void SetBreadth( double bre )
{
breadth = bre;
}
public void SetHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
// 重载 + 运算符来把两个 Box 对象相加
public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.length = b.length + c.length;
box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth;
box.height = b.height + c.height;
return box;
}
}
class Tester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
Box Box3 = new Box(); // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box
double volume = 0.0; // 体积
// Box1 详述
Box1.SetLength(6.0);
Box1.SetBreadth(7.0);
Box1.SetHeight(5.0);
// Box2 详述
Box2.SetLength(12.0);
Box2.SetBreadth(13.0);
Box2.SetHeight(10.0);
// Box1 的体积
volume = Box1.GetVolume();
Console.WriteLine($"Box1 的体积:{volume}");
// Box2 的体积
volume = Box2.GetVolume();
Console.WriteLine($"Box2 的体积:{volume}");
// 把两个对象相加,实际上调用上面的重载函数
Box3 = Box1 + Box2;
// Box3 的体积
volume = Box3.GetVolume();
Console.WriteLine($"Box3 的体积:{volume}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
Box1 的体积: 210
Box2 的体积: 1560
Box3 的体积: 5400
图自菜鸟教程。
其他实例:
using System;
namespace OperatorOvlApplication
{
class Box
{
private double length; // 长度
private double breadth; // 宽度
private double height; // 高度
public double getVolume()
{
return length * breadth * height;
}
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public void setBreadth( double bre )
{
breadth = bre;
}
public void setHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
// 重载 + 运算符来把两个 Box 对象相加
public static Box operator+ (Box b, Box c)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.length = b.length + c.length;
box.breadth = b.breadth + c.breadth;
box.height = b.height + c.height;
return box;
}
public static bool operator == (Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length == rhs.length && lhs.height == rhs.height
&& lhs.breadth == rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public static bool operator !=(Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length != rhs.length || lhs.height != rhs.height
|| lhs.breadth != rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public static bool operator <(Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length < rhs.length && lhs.height
< rhs.height && lhs.breadth < rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public static bool operator >(Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length > rhs.length && lhs.height
> rhs.height && lhs.breadth > rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public static bool operator <=(Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length <= rhs.length && lhs.height
<= rhs.height && lhs.breadth <= rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public static bool operator >=(Box lhs, Box rhs)
{
bool status = false;
if (lhs.length >= rhs.length && lhs.height
>= rhs.height && lhs.breadth >= rhs.breadth)
{
status = true;
}
return status;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("({0}, {1}, {2})", length, breadth, height);
}
}
class Tester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box Box1 = new Box(); // 声明 Box1,类型为 Box
Box Box2 = new Box(); // 声明 Box2,类型为 Box
Box Box3 = new Box(); // 声明 Box3,类型为 Box
Box Box4 = new Box();
double volume = 0.0; // 体积
// Box1 详述
Box1.setLength(6.0);
Box1.setBreadth(7.0);
Box1.setHeight(5.0);
// Box2 详述
Box2.setLength(12.0);
Box2.setBreadth(13.0);
Box2.setHeight(10.0);
// 使用重载的 ToString() 显示两个盒子
Console.WriteLine("Box1: {0}", Box1.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Box2: {0}", Box2.ToString());
// Box1 的体积
volume = Box1.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box1 的体积: {0}", volume);
// Box2 的体积
volume = Box2.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box2 的体积: {0}", volume);
// 把两个对象相加
Box3 = Box1 + Box2;
Console.WriteLine("Box3: {0}", Box3.ToString());
// Box3 的体积
volume = Box3.getVolume();
Console.WriteLine("Box3 的体积: {0}", volume);
//comparing the boxes
if (Box1 > Box2)
Console.WriteLine("Box1 大于 Box2");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box1 不大于 Box2");
if (Box1 < Box2)
Console.WriteLine("Box1 小于 Box2");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box1 不小于 Box2");
if (Box1 >= Box2)
Console.WriteLine("Box1 大于等于 Box2");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box1 不大于等于 Box2");
if (Box1 <= Box2)
Console.WriteLine("Box1 小于等于 Box2");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box1 不小于等于 Box2");
if (Box1 != Box2)
Console.WriteLine("Box1 不等于 Box2");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box1 等于 Box2");
Box4 = Box3;
if (Box3 == Box4)
Console.WriteLine("Box3 等于 Box4");
else
Console.WriteLine("Box3 不等于 Box4");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
输出:
Box1: (6, 7, 5)
Box2: (12, 13, 10)
Box1 的体积: 210
Box2 的体积: 1560
Box3: (18, 20, 15)
Box3 的体积: 5400
Box1 不大于 Box2
Box1 小于 Box2
Box1 不大于等于 Box2
Box1 小于等于 Box2
Box1 不等于 Box2
Box3 等于 Box4
接口
接口(interface)定义了所有类继承接口时应遵循的语法合同,定义了语法合同 “是什么” 部分,派生类定义了语法合同 “怎么做” 部分。
接口定义了 属性、方法 和 事件,这些都是接口的 成员。
接口 只包含了成员的声明,成员的定义是 派生类 的责任,接口提供了派生类应遵循的标准结构。
接口使得实现接口的类或结构在形式上保持一致。
抽象类在某种程度上与接口类似,但是,它们大多只是用在当只有少数方法由基类声明由派生类实现时。
接口本身并不实现任何功能,它只是和声明实现该接口的对象订立一个必须实现哪些行为的契约。
抽象类不能直接实例化,但允许派生出具体的,具有实际功能的类。
接口定义
接口使用 interface 关键字声明,它与类的声明类似,接口声明默认是 public 的,示例:
interface IMyInterface
{
void MethodToImplement();
}
以上代码定义了接口 IMyInterface ,通常接口命名以大写字母 I 开头,这个接口只有一个方法 MethodToImplement() ,没有参数和返回值,当然我们可以按照需求设置参数和返回值。
实例:
using System;
interface IMyInterface
{
// 接口成员
void MethodToImplement();
}
class InterfaceImplementer : IMyInterface
{
static void Main()
{
InterfaceImplementer iImp = new InterfaceImplementer();
iImp.MethodToImplement();
}
public void MethodToImplement()
{
Console.WriteLine("MethodToImplement() called.");
}
}
InterfaceImplementer 类实现了 IMyInterface 接口,接口的实现与类的继承语法格式类似:
class InterfaceImplementer : IMyInterface
继承接口后,需要实现接口的方法 MethodToImplement() , 方法名必须与接口定义的方法名一致。
接口继承
以下实例定义了两个接口 IMyInterface 和 IParentInterface 。
如果一个接口继承其他接口,那么实现类或结构就需要实现所有接口的成员。
以下实例 IMyInterface 继承了 IParentInterface 接口,因此接口实现类必须实现 MethodToImplement() 和 ParentInterfaceMethod() 方法:
using System;
interface IParentInterface
{
void ParentInterfaceMethod();
}
interface IMyInterface : IParentInterface
{
void MethodToImplement();
}
class InterfaceImplementer : IMyInterface
{
static void Main()
{
InterfaceImplementer iImp = new InterfaceImplementer();
iImp.MethodToImplement();
iImp.ParentInterfaceMethod();
}
public void MethodToImplement()
{
Console.WriteLine("MethodToImplement() called.");
}
public void ParentInterfaceMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("ParentInterfaceMethod() called.");
}
}
输出:
MethodToImplement() called.
ParentInterfaceMethod() called.